
Add-on to core solution
BioDiversity
BioDiversity is an add-on that specifies a set of science-based requirements which aim to help producers demonstrate their on-farm biodiversity management practices and retailers to identify suppliers that fulfill their corporate social responsibility pledges.
Monitor and manage key biodiversity indicators
What is BioDiversity?
The BioDiversity add-on functions as the base for a farm-level audit which supports producers in demonstrating their biodiversity management practices to retailers and traders. In turn, supply chain stakeholders may require suppliers to undergo an audit to contribute to fulfilling their corporate social responsibility pledges. Designed to be paired with theIntegrated Farm Assurance (IFA) for fruit and vegetables standard, the audit covers aspects such as soil and nutrients, land restoration measures, and integrated pest management. The add-on strives to monitor and protect key on-farm biodiversity indicators, raising awareness and providing guidance on the development of a comprehensive biodiversity action plan.
BioDiversity at a glance
Audited together
with IFA for fruit and vegetables to minimize the audit burden for producers
Offers cost-efficient audits
for a wide range of fruit and vegetable farm sizes and types, including smallholders and producer groups
Applicable to producers
based in the European Economic Area (EEA)
Integrates continuous improvement
into the farm-level monitoring of biodiversity issues
Establishes knowledge-sharing,
training, and capacity-building tools, as well as off-farm synergies
Supports
the UN Global Compact Food and Agriculture Business Principles
Audited together
with IFA for fruit and vegetables to minimize the audit burden for producers
Integrates continuous improvement
into the farm-level monitoring of biodiversity issues
Offers cost-efficient audits
for a wide range of fruit and vegetable farm sizes and types, including smallholders and producer groups
Establishes knowledge-sharing,
training, and capacity-building tools, as well as off-farm synergies
Applicable to producers
based in the European Economic Area (EEA)
Supports
the UN Global Compact Food and Agriculture Business Principles
Which topics does BioDiversity address?
BioDiversity was developed by a multistakeholder project team on the initiative of the German retailer Lidl in 2020. The collaboration brought together biodiversity expertise from across the supply chain, NGOs, and academia, including Sustainable Food Systems GmbH (SFS), the Global Nature Fund, Bioland, fresh produce suppliers, producers in Spain, Poland, Italy, and Germany, and the Nürtingen-Geislingen University in Germany.
Our approach to standard setting ensures that add-ons to core solutions remain robust, realistic, and cost-efficient while meeting the evolving demands of buyers.
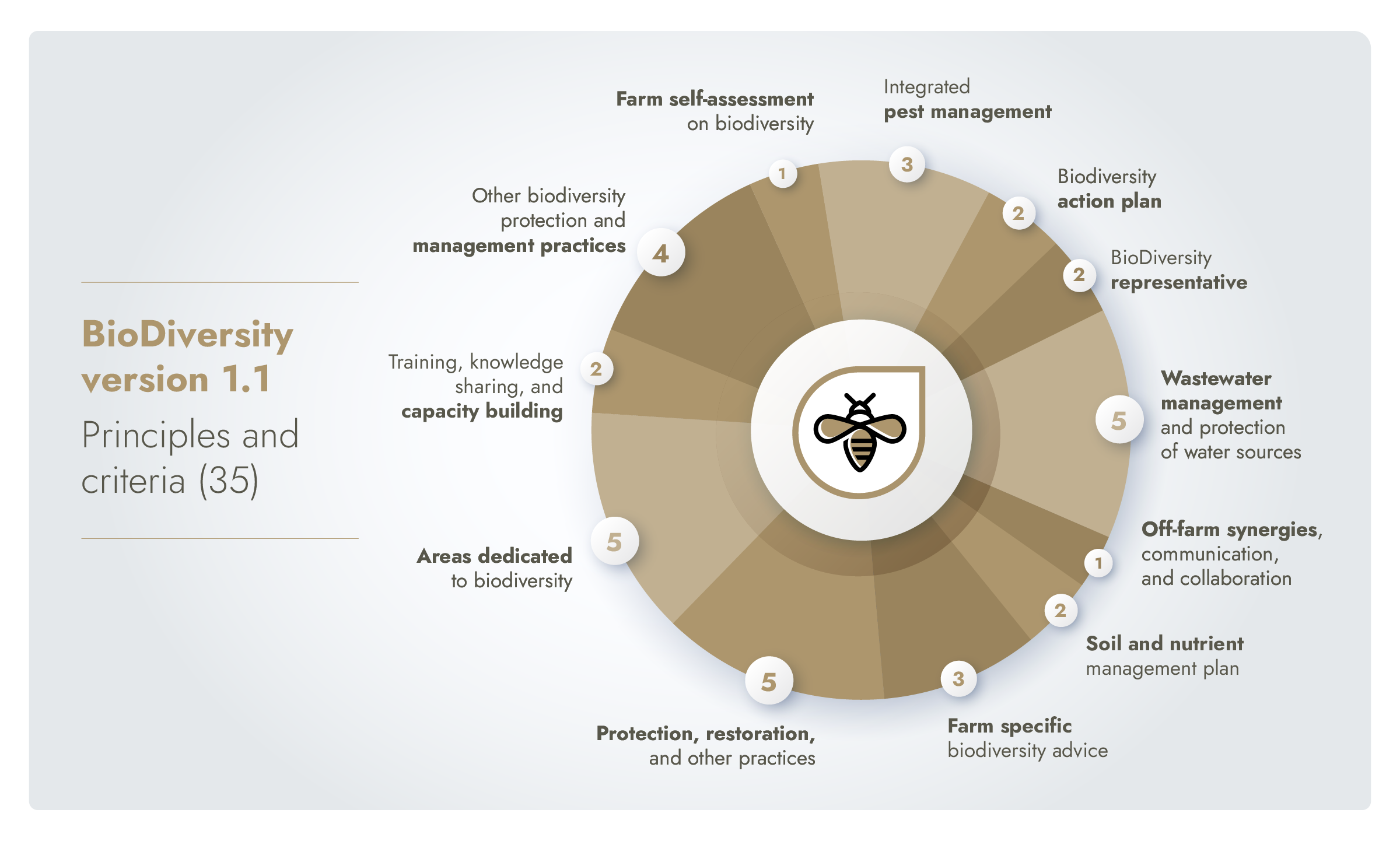
Core topics in BioDiversity v1.1 include:
Biodiversity action plan
Farm areas dedicated to biodiversity
Protection and restoration measures
Soil and nutrient management plan
Integrated pest management
Wastewater management and protection of water sources
Off-farm synergies and collaboration
Training, knowledge sharing, and capacity building
BioDiversity representative
Farm self-assessment on biodiversity
Discover how BioDiversity helps you address challenges in the agricultural sector.

Who should use BioDiversity?
BioDiversity is applicable only to fruit and vegetable producers located in the EEA.
The add-on offers cost-efficient audit options for both individual producers (single site and multisite producers) and producer groups, including smallholders. Producers can get audited in any EEA country where a GLOBALG.A.P. approved certification body (CB) conducts audits.
V1.1 must be used in combination with IFA v6.
How does BioDiversity work?
Compliance with the add-on requirements is audited annually by an accredited and independent third-party CB together with the annual IFA audit (or an audit against a benchmarked scheme/checklist).
Producers can choose from any GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB active in the relevant country – although the same CB which conducts the IFA audit must also conduct the BioDiversity audit.
A successful CB audit results in a letter of conformance valid for one year.
The add-on is composed of principles and criteria (P&Cs). P&Cs are graded in two levels: Major Must and Minor Must.
Principles
Fundamentals that set the foundation of a GLOBALG.A.P. requirement
Written in question form
Describe the outcome to be achieved in the corresponding criteria.
Criteria
Methods that producers can use to demonstrate a principle to be true
Compliance can be demonstrated in different ways, e.g., data, record of procedure
Evidence must demonstrate that the outcome is achieved
Read more about the audit process and add-on requirements.
How is conformance status verified?
Every producer registered in the GLOBALG.A.P. certification system is assigned a 13-digit GLOBALG.A.P. identification number (e.g., a GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN)). This number allows verification of conformance status in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform, upholding our rigorous transparency requirements throughout the supply chain.
Producers can control data access and privacy rights for audit reports, and the reports are not shared publicly or with third parties. This process is handled via your chosen CB.

Corporate news and events have moved!
All the latest updates can now be found on the Agraya website – connecting people, ideas, and solutions across the global farming network.
Looking for technical news?
Technical news updates for all add-ons can be found in our technical news libraries.
Contribute to ecosystem health and resilience
Why choose BioDiversity?
Biodiversity – the huge variety of life on earth, encompassing animals, plants, bacteria, and fungi – is one of the world’s most precious resources. The protection, restoration, and enhancement of on-farm biodiversity is under increasing scrutiny across the value chain and now represents a major concern for brand owners, retailers, and consumers alike. BioDiversity offers a practical and cost-efficient path for producers to implement and demonstrate farm-level best practices that help contribute to the health and conservation of surrounding ecosystems.
Which industry challenges does BioDiversity address?
The impact of biodiversity on agricultural production is considered in numerous influential international frameworks such as the UN Sustainable Development Goals and the EU’s European Green Deal.
As a result, sector transformation is increasingly expected by both civil society and major retail and food production chains – highlighting the need for coordinated action from all stakeholders.
The EU’s 2030 Biodiversity Strategy and Farm to Fork Strategy aim to put Europe's biodiversity on a path to recovery – with producers playing a positive and growing role.
Industry solutions are therefore needed to monitor and demonstrate how agricultural enterprises promote and enhance biodiversity at farm level.
BioDiversity is a cost-efficient add-on for fruit and vegetable producers with production processes certified to the IFA standard that complements rather than competes with existing certification systems.
Follow our five steps to BioDiversity to get started today.
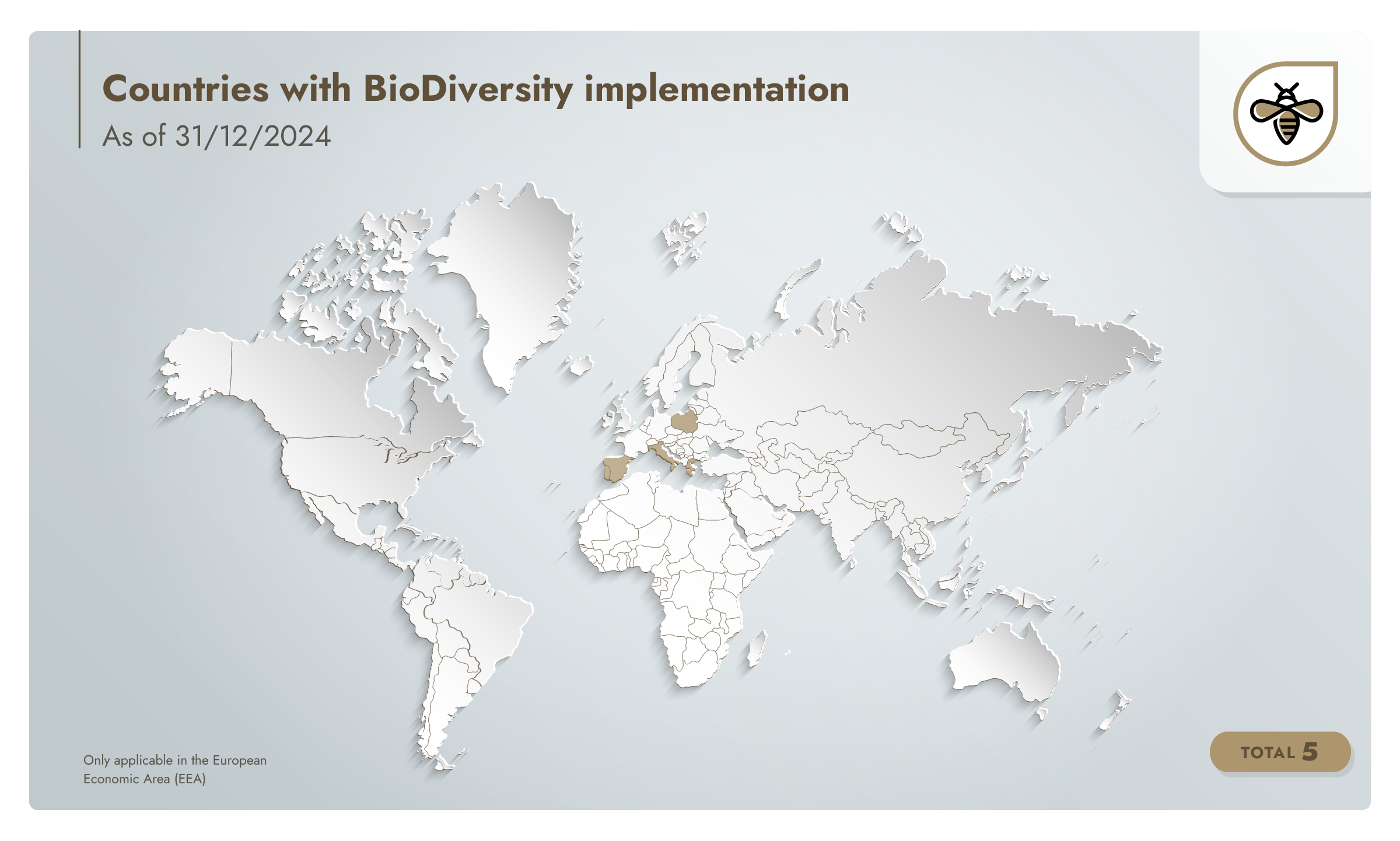
BioDiversity in numbers (as of 31/12/2024)
1,278
producers audited to the add-on
5
countries with audited production processes
12,763
hectares of audited production
1,278
producers audited to the add-on
5
countries with audited production processes
12,763
hectares of audited production

What are the benefits for producers?
Develop an effective biodiversity action plan and demonstrate your management of on-farm biodiversity.
Implement an outcome-based and scientifically sound methodology, recognizing farm-specific biodiversity realities.
Leverage synergies with IFA for fruit and vegetables, as well as other add-ons to core solutions such as the Sustainable Program for Irrigation and Groundwater Use (SPRING) add-on.
Apply our farm assurance solutions on a wide range of farm types and sizes, and access certification options for both individual producers and producer groups.
Benefit from a cost-efficient audit process which produces reliable data, improving transparency and risk monitoring in supply chains.

What are the benefits for supply chain stakeholders?
Implement a fit-for-purpose add-on developed by the sector, for the sector, that helps fulfill corporate social responsibility pledges.
Support alignment with relevant civil society stakeholders and international frameworks such as the EU’s European Green Deal.
Boost transparency and risk monitoring, and integrate a continuous improvement mechanism at farm level.
Further demonstrate commitment to more responsible farming practices by building on established principles and criteria in IFA for fruit and vegetables.
Access a flexible portfolio of farm assurance solutions that provides all the coverage you need through one certification system – including other add-ons such as SPRING and the Impact-Driven Approach to Sustainability (IDA).

Maintaining trust in GLOBALG.A.P. certification
The GLOBALG.A.P. Integrity Program was founded in 2008 as the first of its kind in food certification. Designed to ensure the consistent delivery and implementation of GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons worldwide, the program monitors and assesses all aspects of the third-party certification process.
Which solutions can be combined with BioDiversity?
BioDiversity is designed to be paired with IFA certification for fruit and vegetables. Audits are conducted together with the IFA audit, allowing producers to extend their certification scope flexibly and efficiently through a single audit.
Learn more about GLOBALG.A.P. smart farm assurance solutions.
You may also be interested in...
Integrated Farm Assurance for fruit and vegetables
IFA is a global standard that aims to promote safer and more responsible farming practices in fruit and vegetable production.
Sustainable Program for Irrigation and Groundwater Use
SPRING is a farm-level add-on that aims to promote responsible water management in plant production processes.
Impact-Driven Approach to Sustainability add-on
The IDA add-on aims to promote more responsible farming practices through the collection and analysis of input consumption data and other farm metrics.
Your guide to implementation
How to prepare for a BioDiversity audit
Learn more about the key documents and fee structure of BioDiversity. Follow our five steps to BioDiversity for an overview of the audit process, and find a GLOBALG.A.P. approved certification body (CB) in your area to get started.
Implementation and CB audit process
How does the CB audit process work?
Designed to complement existing Integrated Farm Assurance (IFA) certification, compliance with the BioDiversity requirements is audited annually together with the IFA audit by accredited and independent third-party CBs.
Producers can choose from any GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB active in the relevant country – although the same CB which conducts your IFA audit must also conduct the BioDiversity audit.
A successful CB audit results in a letter of conformance valid for one year.
The CB is responsible for uploading the audit reports and maintaining the accuracy of producer data in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform.
Producers will be audited annually by a CB as part of the renewal process.
Which documents are required?
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations and GLOBALG.A.P. BioDiversity general rules specifications: Rules that define how the audit process works, from the scope of the add-on to the audit requirements.
Principles and criteria (P&Cs): Principles are the fundamental requirements for each add-on. They describe the outcome to achieve and are accompanied by corresponding criteria that detail the various ways in which a producer can demonstrate compliance.
Checklist: The full list of add-on criteria as used by CB auditors, enabling producers to conduct a self-assessment in preparation for the CB audit.
Guidelines: A supporting document that clarifies terminology and outlines procedures to help producers comply with the add-on requirements.
Which version of BioDiversity is currently valid?
There is currently one version of BioDiversity available for audit.
BioDiversity v1.1 was published in December 2023. It replaced v1 on 1 January 2024.
The FAQ contains more information on documents, the renewal process, and more.

What are the BioDiversity add-on requirements?
P&Cs are graded in two levels: Major Must and Minor Must.
To pass a CB audit, producers must comply with 100% of the Major Must principles and at least 75% of the Minor Must principles.
Corrective actions must be proposed for all non-compliances and submitted to the CB within the specified period.
Non-compliances must then be verified as corrected and compliant by the CB before a letter of conformance can be issued.
How much does a BioDiversity audit cost?
Each farm is unique, and the total audit costs depend on a combination of factors such as farm size, number of sites, location, necessary preparation measures (such as establishing new procedures), and more.
BioDiversity contains three cost elements:
1. Implementation costs: Incurred by the producer to prepare for the CB audit
2. CB service fees: Determined and invoiced by the CB to cover audit time and travel costs
3. GLOBALG.A.P. assessment license fee: Calculated based on the audit option
The GLOBALG.A.P. fee table contains full information on the fee structure for each standard and add-on.
Five steps to BioDiversity

You will need the GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations, the GLOBALG.A.P. BioDiversity general rules specifications, the BioDiversity P&Cs, and the checklist. All of the required documents are available online, for free, and in multiple languages. They are linked below and can also be found in the GLOBALG.A.P. document center.

Use the documents to guide the implementation of the add-on requirements, and then
conduct a self-assessment using the checklist. Our worldwide network of Registered Trainers
can also provide assistance during audit preparations.

Search the list of GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs by region, country, scope, and status. Contact the CB of your choice and request an audit. Note that the GLOBALG.A.P. fee table does not cover CB service fees such as audit time or travel costs to your site.

The CB will perform the on-site audit and upload the results to the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform. Any non-compliances which are detected during the audit must be corrected within the specified period and verified by the CB before a letter of conformance can be issued.

Once all requirements are met and verified by the CB, they will issue your BioDiversity letter of conformance. Your conformance status is then publicly visible in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform for transparency in the market.
Key documents
The three most relevant documents are linked below. Click ‘view more’ to see further related documents. Remember to always check with your CB that you have all necessary documents prior to audit.
BioDiversity
Checklists
V1.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
xlsx
Checklists
V1.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
xlsx
Checklists are documents containing standard/add-on principles and criteria which are used during the audit/assessment to check whether compliance is achieved. They may also be used to conduct self-assessments.
BioDiversity
Principles and criteria (P&Cs) (CPCCs)
V1.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Principles and criteria (P&Cs) (CPCCs)
V1.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Principles and criteria are a complete list of the requirements for a given standard or add-on. The foundational requirements each detail an outcome that must be achieved, and the corresponding ways in which compliance can be demonstrated.
BioDiversity
Rules and regulations
V1.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Rules and regulations
V1.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Rules and regulations define how a specific standard must be implemented – from the certification scope to the audit requirements for certification bodies.
GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs
The list of GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs can be filtered by region, country, scope, and status. Click a CB to find more information and contact details.
If you do not filter your search, or filter only according to region and/or country, your search results will also show CBs that offer certification against benchmarked schemes, but which may not have approval for any GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons.
A brief history of BioDiversity
The concept for BioDiversity is developed by a multistakeholder project team on the initiative of the German retailer Lidl. The collaboration involves representatives from the supply chain, NGOs, and academia, including Sustainable Food Systems GmbH (SFS), the Global Nature Fund, Bioland, fresh produce suppliers, producers in Spain, Poland, Italy, and Germany, and the Nürtingen-Geislingen University.
From November 2020 to March 2021, GLOBALG.A.P. works with Sustainable Food Systems GmbH (SFS) on the development of the initial criteria set. This involves the identification of relevant biodiversity topics and goals. Between April 2021 and December 2021, the criteria set is refined and developed into a practical and economically viable add-on. This includes the alignment of the checklist with IFA v5, validation of the concept in field trials, creation of guidelines and training material for CBs, and translation of the documents. Version 1 of the add-on is launched in February 2022.
Due to increasing international interest in the add-on, field trials are conducted outside of Europe for the first time in Costa Rica and South Africa. By the end of 2022, there are 178 audited producers across four countries. Alignment of the add-on with IFA v6 begins in late 2022, with the updated BioDiversity v1.1 launching in December 2023. By the end of 2023, there are 1,383 producers under assessment in six countries, marking a rise of over 670% on the previous year.
FAQ
BioDiversity v1.1 replaced v1 on 1 January 2024. It must be combined with Integrated Farm Assurance (IFA) v6 Smart/GFS for fruit and vegetables.
Each farm is unique, and the total audit costs depend on a combination of factors (size, location, existing policies and processes, etc.). The invoice from your certification body (CB) will include CB service fees to cover expenditures (determined by the CB) and the GLOBALG.A.P. assessment license fee.
Download the GLOBALG.A.P. fee table to learn more.
The Biodiversity v1.1 documents are currently available in English only.
All documents are located in the GLOBALG.A.P. document center. More languages are added based on demand – please contact us with requests.
Compliance with the BioDiversity requirements is audited annually. The certification body (CB) audit must take place within the validity period of the current letter of conformance in order for your production processes to retain the conformance status. Contact your CB to request an audit.
Technical questions can be addressed to standard_support@agraya.com. Your query will be forwarded to the relevant technical expert.
The GLOBALG.A.P. Academy offers public trainings on our portfolio of smart farm assurance solutions, while our worldwide network of Registered Trainers offers authorized trainings and other services. See the GLOBALG.A.P. Academy course catalog or find a Registered Trainer for more information.
The CB auditors requirements for BioDiversity are detailed in the “GLOBALG.A.P. BioDiversity general rules specifications”.
Learn more about how to become a GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB or extend your auditing scope.
No, certification to a GLOBALG.A.P. standard/holding a GLOBALG.A.P. certificate is not the same as being a GLOBALG.A.P. Community Member.
GLOBALG.A.P. Community Membership is a paid partnership opportunity, offering a variety of benefits including the ability to support the development of GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons, contribute to the GLOBALG.A.P. governance structure, and access discounted services.
Learn more about how to become a GLOBALG.A.P. Community Member.
GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks may only be used in a strictly B2B context and must be accompanied by a GLOBALG.A.P. identification number (e.g., the producer’s GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN)) or a QR code linked to the producer’s conformance status in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform. The trademarks should never appear to consumers, for example on product packaging.
Download the GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks use: policy and guidelines and the GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks use: FAQ documents for comprehensive information on rules and use cases.
Technical FAQ
No, not per se. What is decisive is whether the area represents a true contribution to biodiversity as described in the guidance documents. If the production area for organic products meets the description, it can be counted (see the BioDiversity v1 guidance document, pages 17–19).
Yes, the areas can be outside of the production area and within the legal farm area, i.e., the total area of the farm. If the producer cannot comply with this requirement (see CP 7.1.1), and all possible measures to establish areas dedicated to biodiversity have been exhausted within the scope of the farm, the biodiversity action plan shall indicate this and biodiversity compensation areas shall be sought (see CP 7.1.3).
Most linear landscape features have a width. For example, hedges tend to be at least half a meter wide. In such cases, you should multiply the length and the width of these features. In other cases, we recommend that producers make an estimation.
The requirements for training are intentionally not prescriptive. No specific training is required, for example, by a certification body. However, it is necessary to explain what type of training was completed, e.g., training through a local network or national project. This enables the sharing of experiences and the multiplication of best practices on how to enhance biodiversity potential.
Such areas are not clearly defined. For the BioDiversity add-on and in the context of Europe, it is recommended to use areas under the Natura 2000 Network as a starting point. The concept of high conservation value areas (HCVAs) largely finds application in a global context. HCVAs are defined as natural habitats where ecological values are considered to be of outstanding significance or critical importance for species diversity, landscapes, ecosystems, habitats, ecosystem services, community needs, and cultural values. In the EU, a similar concept has been developed that is directly related to farming, known as high nature value farmland (HNVF) or areas. The goal is to maintain a high level of biodiversity.
The use of neonicotinoids is generally not permitted under the BioDiversity add-on. However, in extreme emergency cases, such as the risk of complete crop loss, approval for the emergency use of acetamiprid may be granted by your certification body (CB). Permission must be sought from the CB prior to the application of acetamiprid and, if granted, will be considered valid for the whole season. If the CB does not answer in due time, evidence of a formal request is considered sufficient.
Biodiversity is based on complex processes that happen over time in various spatial dimensions and are knowledge intensive. This requires good spatial and temporal planning. Therefore, BioDiversity introduces tools, for example the self-assessment and the BAP, that support producers in tackling the aspects of time and space, while the requirements provide input on topics relevant to biodiversity. Planning with a BAP helps to ensure ongoing operational processes without compromising on economic continuity.
GLOBALG.A.P. views the rollout phase of BioDiversity as a learning curve that will help us all to understand both where existing knowledge has been gained, and how we can support the sharing of experience and help users connect with each other. See the BioDiversity v1 guidance document and the control points regarding advice and training (see CPCCs 4 and 5) for more information.
Control point 8.2.3 of the BioDiversity add-on requires knowledge and awareness, but not action at this point. However, it aims to address more than the relevance of an invasive pest for agricultural production and to also consider biodiversity.
The current version of the BioDiversity add-on only focuses on permanent water bodies.
Parallel ownership is not allowed under BioDiversity. The legal entity that is registered for the add-on shall not buy products originating from production processes that are certified to IFA but not audited to BioDiversity.
The relevant rule (GLOBALG.A.P. BioDiversity general rules specifications version 1, 5.1 a) has been amended, allowing Option 2 producer groups and Option 1 multisite producers to split. This means that not all producer group members and/or production sites need to participate in the add-on audit. The individual GLOBALG.A.P. Numbers (GGNs) are listed on the producer group’s certificate, and it is the buyer’s responsibility to follow-up on those individual GGNs.

Contact us
For technical/interpretation questions, please contact us at standard_support@agraya.com.
For questions about the audit process or the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform, please contact us at customer_support@globalgap.org.