
Core solution
GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody
The GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody (CoC) standard aims to establish procedures that help ensure any product sold with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim or bearing a GGN label logo is truly sourced from a GLOBALG.A.P. certified production process.
Facilitating transparency from farm to retailer
What is GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody?
GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody (CoC) allows supply chain stakeholders to demonstrate management systems that seek to protect the segregation, identification, and traceability of products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes. This way, products produced in line with certified farm-level processes can be connected with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim at the end of the chain – reducing integrity risks, providing reassurance to customers, and adding value to a brand in the market. Applicable to products originating from production processes certified to the Integrated Farm Assurance (IFA) or Compound Feed Manufacturing (CFM) standards, CoC is tried, tested, and trusted around the world, with certificate holders operating in over 60 countries.
CoC at a glance
Applies to a wide range
of types and sizes of supply chain companies – from packers and processors to retailers and restaurants
Connects certified
farming practices with a transparent GLOBALG.A.P. claim at the end of a custodial sequence
Reduces risk
of substitution, dilution, and misidentification of products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes
Relevant for supply chain
companies sourcing from IFA- or CFM-certified production processes
Establishes consistent
certification requirements and monitoring tools, mitigating the risk of food fraud or traceability issues
Covers all products
under the IFA scopes of plants and aquaculture, and animal feed produced under CFM
Applies to a wide range
of types and sizes of supply chain companies – from packers and processors to retailers and restaurants
Relevant for supply chain
companies sourcing from IFA- or CFM-certified production processes
Connects certified
farming practices with a transparent GLOBALG.A.P. claim at the end of a custodial sequence
Establishes consistent
certification requirements and monitoring tools, mitigating the risk of food fraud or traceability issues
Reduces risk
of substitution, dilution, and misidentification of products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes
Covers all products
under the IFA scopes of plants and aquaculture, and animal feed produced under CFM
What is a GLOBALG.A.P. claim?
A GLOBALG.A.P. claim occurs when a GLOBALG.A.P. certificate holder, or a holder of a certificate for a benchmarked scheme or checklist, states and/or markets in a B2B context that a process, service, or product complies with a GLOBALG.A.P. standard or add-on. This includes on-product labeling with a GLOBALG.A.P. identification number.
The visual elements of the consumer-facing GGN label refer to the GGN label logo, the GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN) and/or CoC Number of the GGN label license holder, and the GGN label claim when applied to any product (packaging).
Which topics does CoC address?
International supply chains contain multiple stages. This means that not all supply chain companies source directly from producers with GLOBALG.A.P. certification. CoC is designed to identify products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes and safeguard this status at every stage of the supply chain.
CoC is built on five key principles:
Supply chain companies must purchase products with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim from certified suppliers.
Products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes must be separated from products originating from noncertified production processes at all times.
Products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes must be clearly identified.
Products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes must be traceable.
The company management system must ensure compliance with the CoC requirements.
Continuously improved through collaboration with sector experts and our worldwide network of GLOBALG.A.P. Community Members, our approach to standard setting ensures that CoC remains robust, realistic, and cost-efficient while meeting evolving market demands.
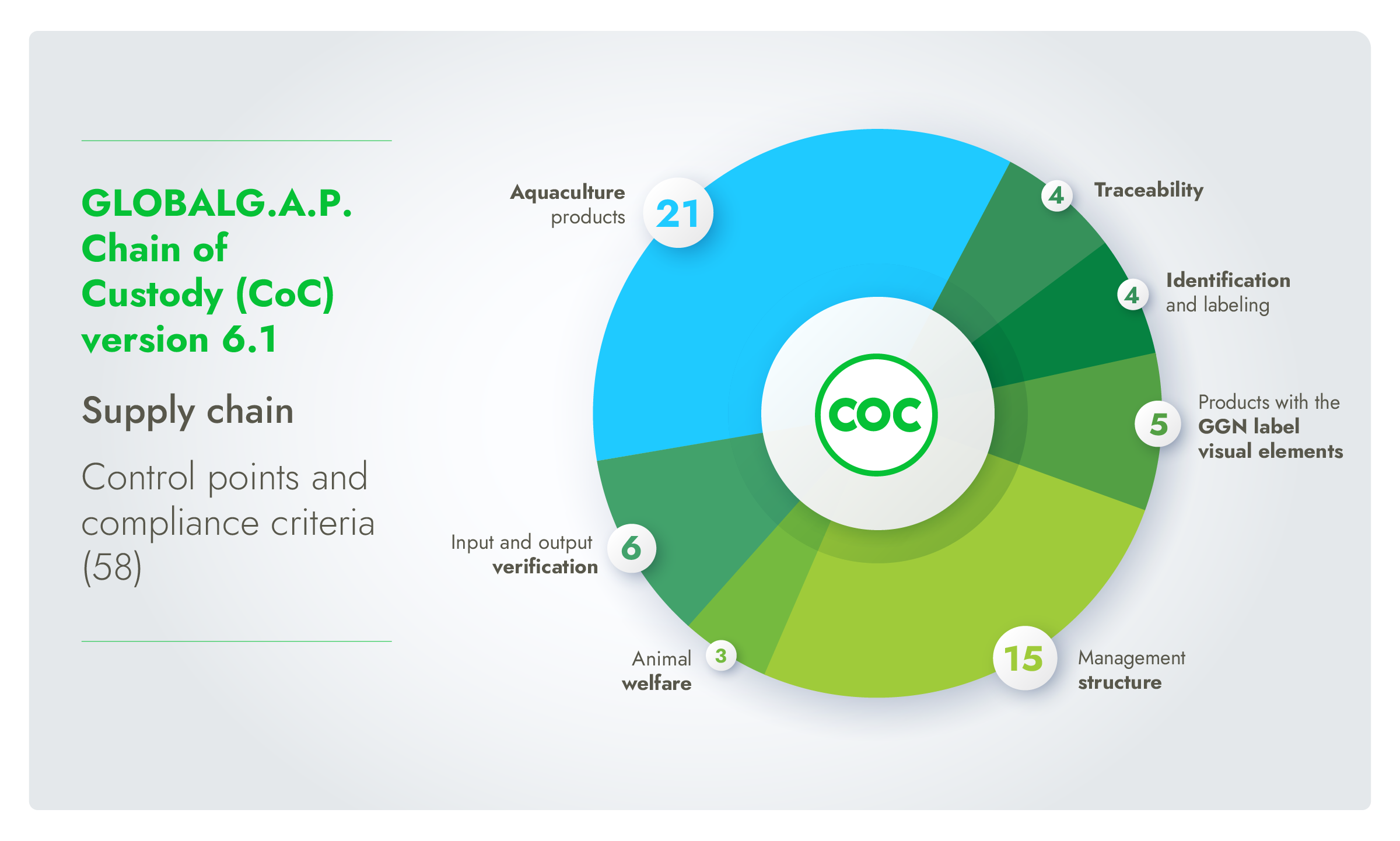
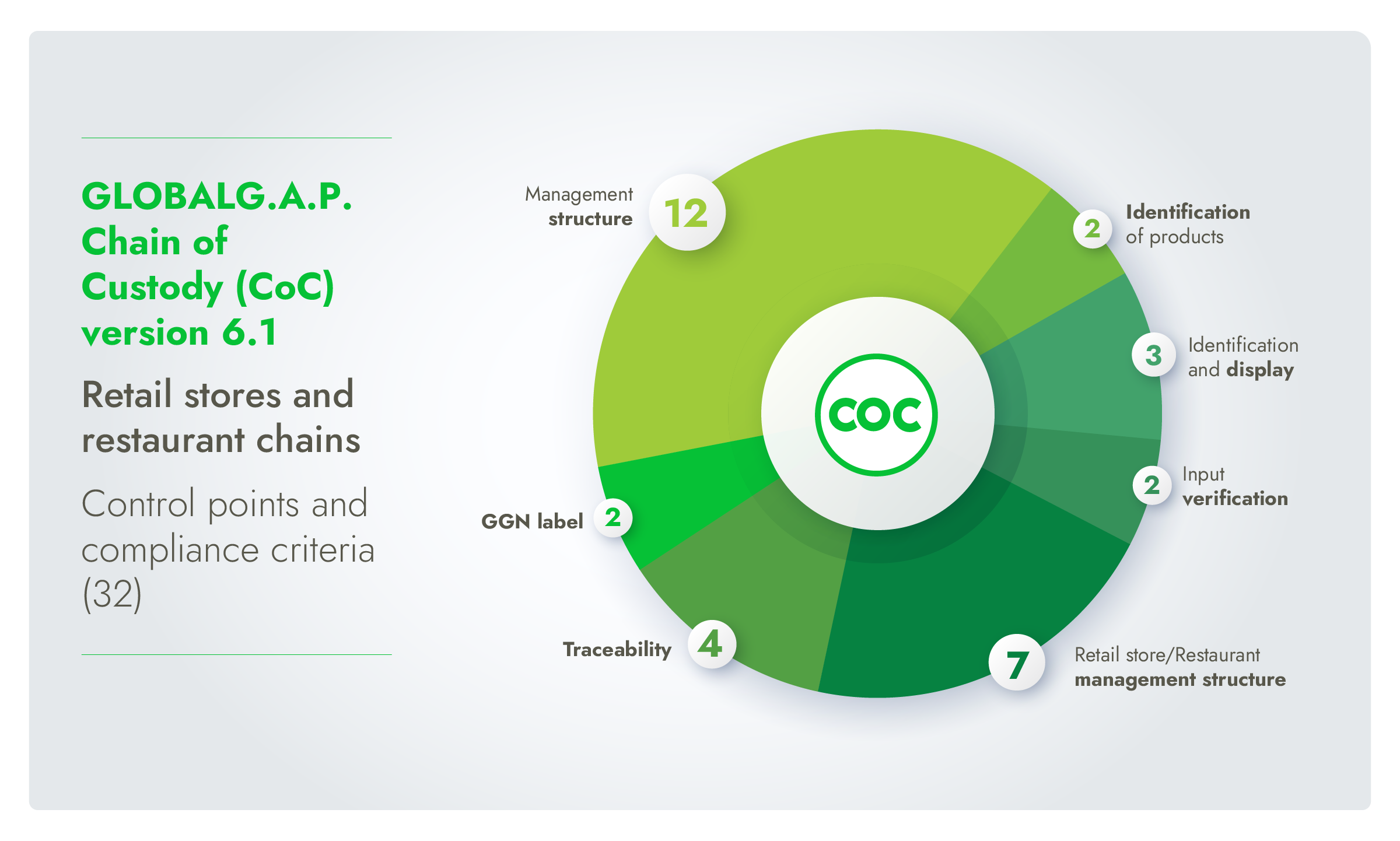
Core topics in CoC v6.1 include:
Management structure
Retail store/Restaurant management structure
Input and output verification
Traceability
Identification and labeling
Identification and display
Products with the GGN label visual elements
Aquaculture products
Animal welfare
Food safety and exceedances
Discover more about how CoC helps you address supply chain challenges.

Who should use CoC?
CoC is an essential tool for any company handling or trading in products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes. The standard applies to a wide range of types and sizes of companies in the supply chain that sell products with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim, including subcontractors who handle the products:
Producers
Packers
Brokers
Processors
Logistics companies
Retailers
Restaurants
The standard covers all products under the IFA scopes of plants and aquaculture, as well as animal feed produced under the CFM standard.
CoC certification is available for companies (legal entities) under Option 1, meaning that if the company operates more than one site, all sites must be audited individually.
Stakeholders to which CoC certification does not apply
For example, the process of producing and packing the same product cannot be certified under both IFA and CoC.
For example, companies that trade or handle products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes without identifying the products as originating from a certified production process or selling the products with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim cannot achieve CoC certification.
For example, wholesaler stores’ own self-service distribution sites (such as wholesale cash and carry) cannot get certification unless the products are sold exclusively to other companies (which are not their own retail stores).
For example, companies responsible for the preparation of shipping and export documents, booking cargo space, negotiating freight charges, freight consolidation, cargo insurance, customs clearance, and/or filing insurance claims cannot get CoC certification.
How does CoC work?
Compliance with the standard requirements is audited annually by an accredited and independent third-party certification body (CB).
Companies can choose from any GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB active in the relevant country
A successful CB audit results in a certificate valid for one year.
The standard is composed of control points and compliance criteria (CPCCs). CPCCs are graded in three levels: Major Must, Minor Must, and Recommendation.
Control points
Fundamentals that set the foundation of a GLOBALG.A.P. requirement
Written in question form
Compliance criteria
Methods that producers can use to demonstrate a control point to be true
Evidence required for demonstrating that the outcome is achieved
Read more about the audit process and standard requirements.
How is certification status verified?
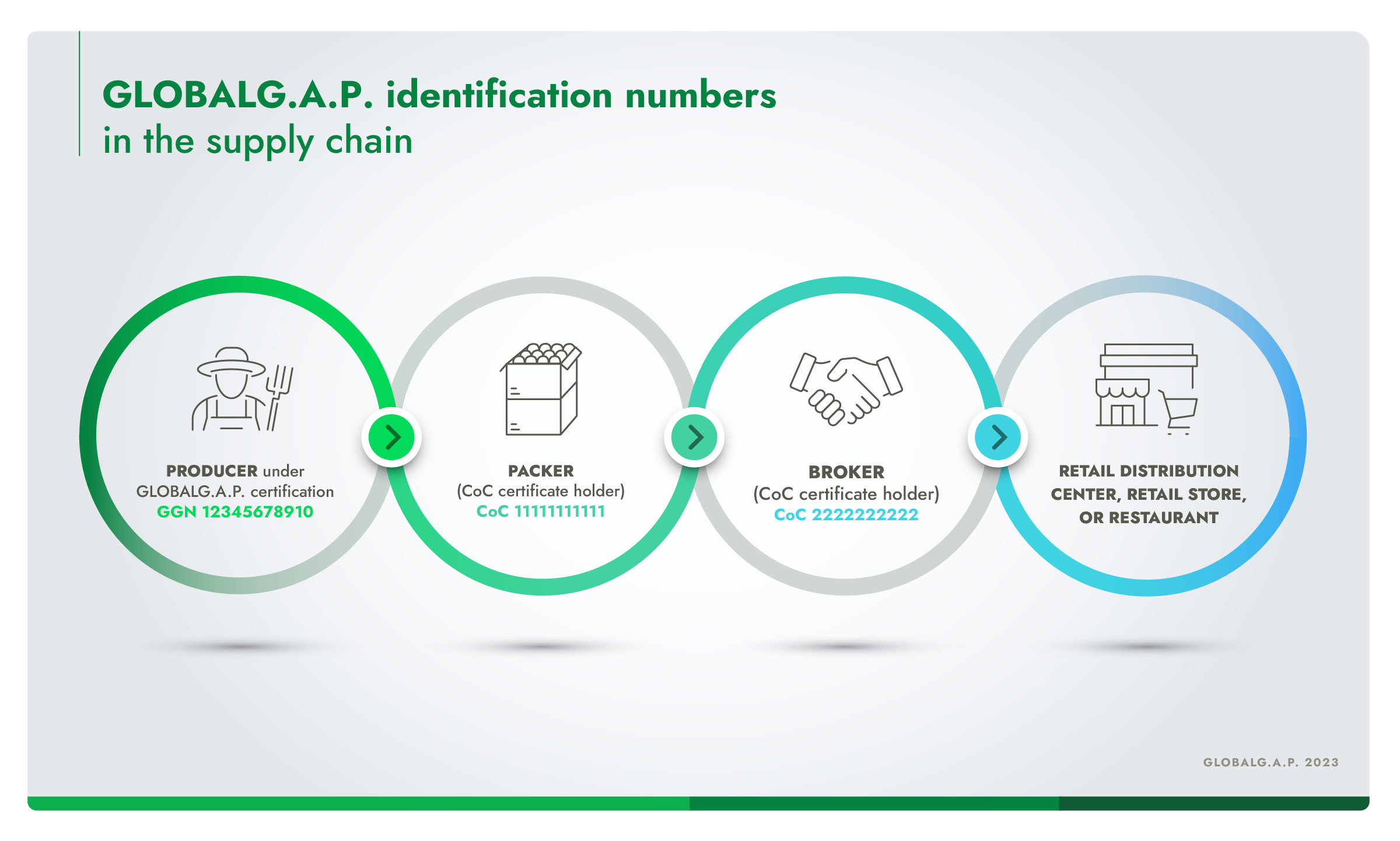
Every supply chain company registered in the GLOBALG.A.P. certification system is assigned a 13-digit GLOBALG.A.P. identification number such as a GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN) or a CoC Number. A GGN is linked to a producer (any activity related to IFA or CFM), while a CoC Number is linked to a company with CoC certification (any activity related to the supply chain).
These numbers are linked to a legal entity – a producer or supply chain company – for as long as that entity exists. This allows verification of certification status in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform, upholding our rigorous transparency requirements throughout the supply chain.
Supply chain stakeholders can control data access and privacy rights for audit reports, and the reports are not shared publicly or with third parties. This process is handled via your chosen CB.
Combined CoC audits
As part of our mission to reduce duplication in supply chains, we have worked in collaboration with other certification schemes to offer combined audits with the GLOBALG.A.P. CoC standard.
The following options are not GLOBALG.A.P. benchmarked schemes, but offer a combined audit approach designed to save resources by auditing only the parts of the CoC checklist that are not covered by the below standards:
CoC through BRCGS
BRCGS Food Safety standardsCoC through IFS
IFS Food Safety standardsCoC through QS
QS Wholesale Fruit, Vegetables, PotatoesCoC through AMA
AMA Quality Seal Guideline “Fruits, Vegetables, Potatoes”
Only GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs may conduct the CoC combined audits, and a successful audit will result in two separate certificates. Certification status is then visible in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform for transparency in the market.

Corporate news and events have moved!
All the latest updates can now be found on the Agraya website – connecting people, ideas, and solutions across the global farming network.
Looking for technical news?
Technical news updates for core solutions can be found in our technical news libraries.
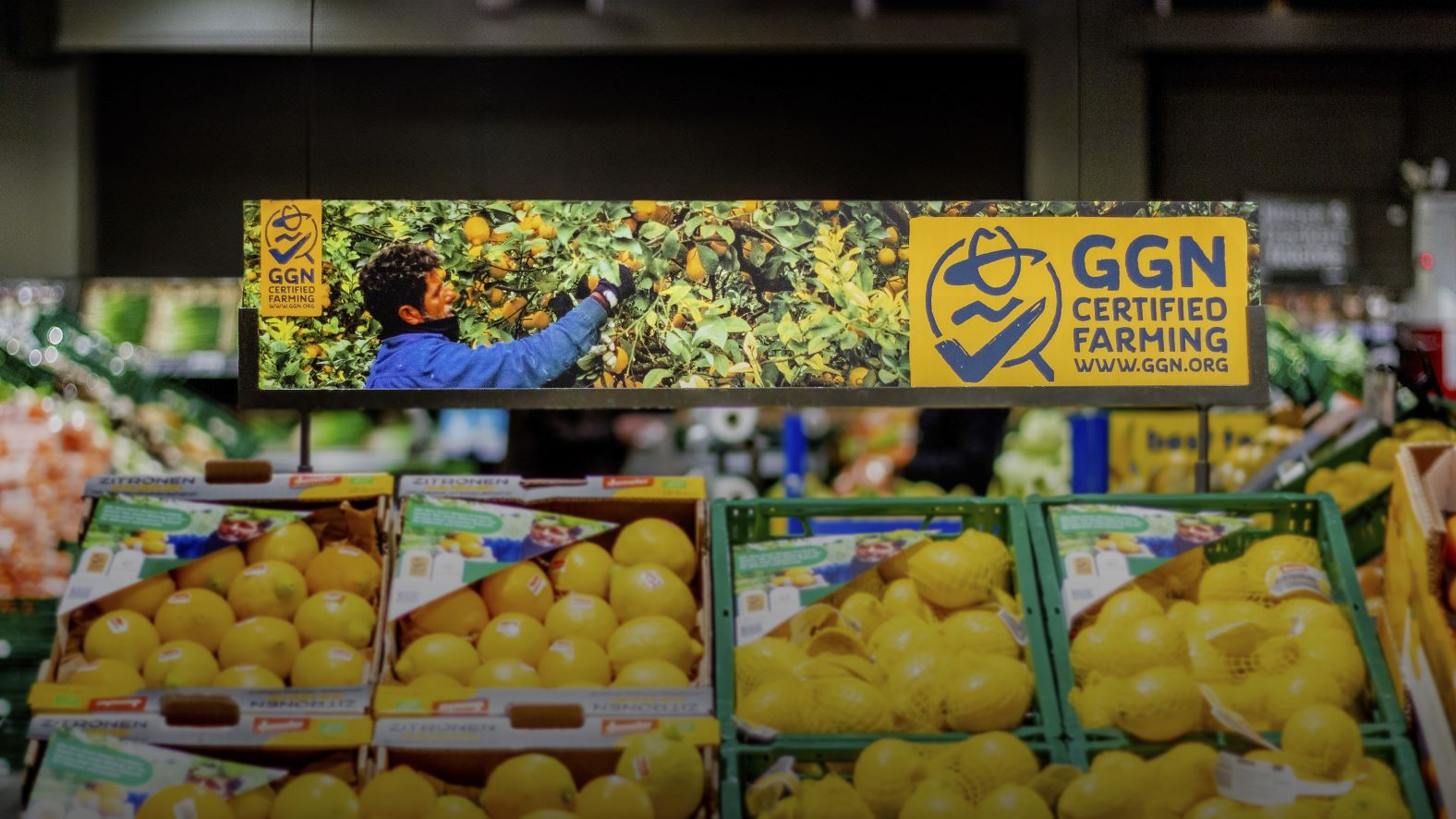

Making responsible farming visible to consumers
CoC certification is one of the requirements for using the GGN label – a consumer label for certified, responsible farming and transparency found on fruit and vegetables, farmed seafood, flowers, and plants. Improve your competitive edge and grow trust in your brand by making responsible farming visible on store shelves!
Safeguard supply chain integrity
Why choose GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody?
GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody (CoC) certification strives to protect the integrity of products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes. Requested by buyers across the globe, the standard outlines a practical path for supply chain companies to implement and demonstrate management systems for the handling and trading of these products. CoC therefore helps mitigate reputational risks and builds confidence in increasingly complex global value chains.
Which industry challenges does CoC address?
Implementing safer and more responsible farming practices is a core demand of retailers and consumers around the world.
Achieving recognition for these practices through certification takes significant time, effort, and investment from producers at farm level.
However, the value of responsible farming practices is significantly reduced if they cannot be transparently linked to a GLOBALG.A.P. claim at the end of the supply chain.
If segregation and traceability are lacking, the reputational risk for buyers increases – through food fraud or the inability to trace a product if, for example, a food safety issue arises.
Supply chain companies therefore need consistent certification requirements and monitoring tools to ensure that the integrity of products is protected up to the final sale.
As global supply chains grow in complexity, CoC certification provides reassurance to customers and adds value to a brand in the market.
Follow our five steps to certification to get started today.
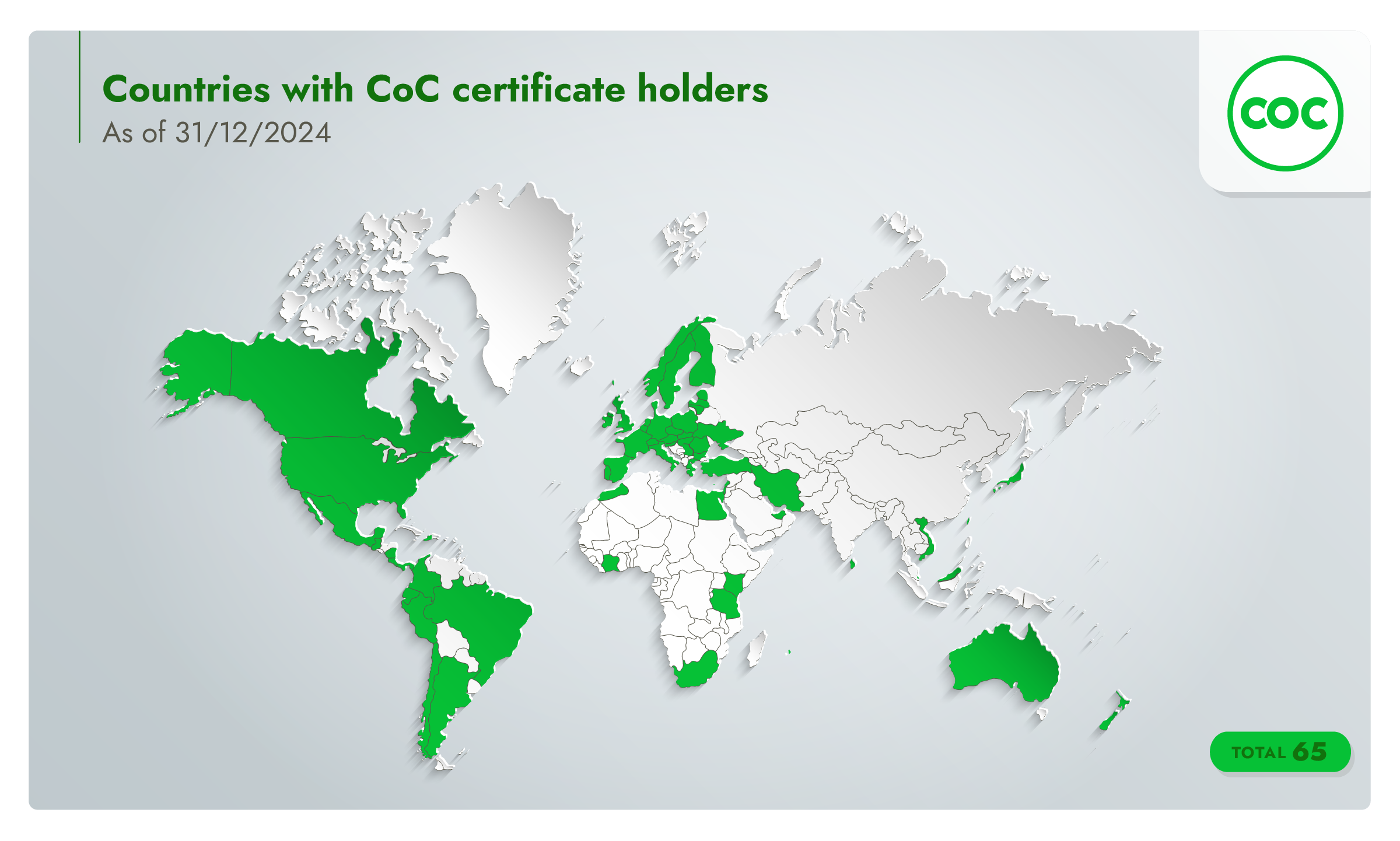
CoC in numbers (as of 31/12/2024)
5,137
companies under certification
65
countries with CoC certificate holders
153
traders with CoC certification participating in the GGN label initiative
5,137
companies under certification
65
countries with CoC certificate holders
153
traders with CoC certification participating in the GGN label initiative

What are the benefits for supply chain companies?
Reduce the risk of substitution, dilution, and misidentification of products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes
Improve segregation methods and traceability systems in the supply chain
Enable a quick response if issues arise through transparency and risk monitoring
Reflect the certified company’s commitment towards safer and more responsible farming practices
Apply the standard to a wide range of types and sizes of supply chain companies globally
Add value to brands in the market and provide assurance to customers
A few years ago, we started our path with GLOBALG.A.P. CoC certification. It has certainly helped us to strengthen our policies and has opened doors for us to work with certain clients. Both GLOBALG.A.P. and our CB have been supporting us with any doubts that have arisen, making the certification process easy and agile.
Victor Abad Lopez
Quality and Food Safety Head Manager at Compesca | Spain

Maintaining trust in GLOBALG.A.P. certification
The GLOBALG.A.P. Integrity Program was founded in 2008 as the first of its kind in food certification. Designed to ensure the consistent delivery and implementation of GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons worldwide, the program monitors and assesses all aspects of the third-party certification process.
Which solutions can be combined with CoC?
We offer a range of standards and add-ons targeted to specific aspects of production and the supply chain.
Learn more about GLOBALG.A.P. smart farm assurance solutions.
You may also be interested in...
Integrated Farm Assurance for fruit and vegetables
IFA is a global standard that aims to promote safer and more responsible farming practices in fruit and vegetable production.
Integrated Farm Assurance for flowers and ornamentals
IFA is a global standard that aims to promote safer and more responsible farming practices in flower and ornamentals production.
Integrated Farm Assurance for aquaculture
IFA is a global standard that aims to promote safer and more responsible farming practices in aquaculture production.
Your guide to implementation
How to prepare for a GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody audit
Learn more about the key documents and fee structure of GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody (CoC). Follow our five steps to certification for an overview of the certification process, and find a GLOBALG.A.P. approved certification body (CB) in your area to get started.
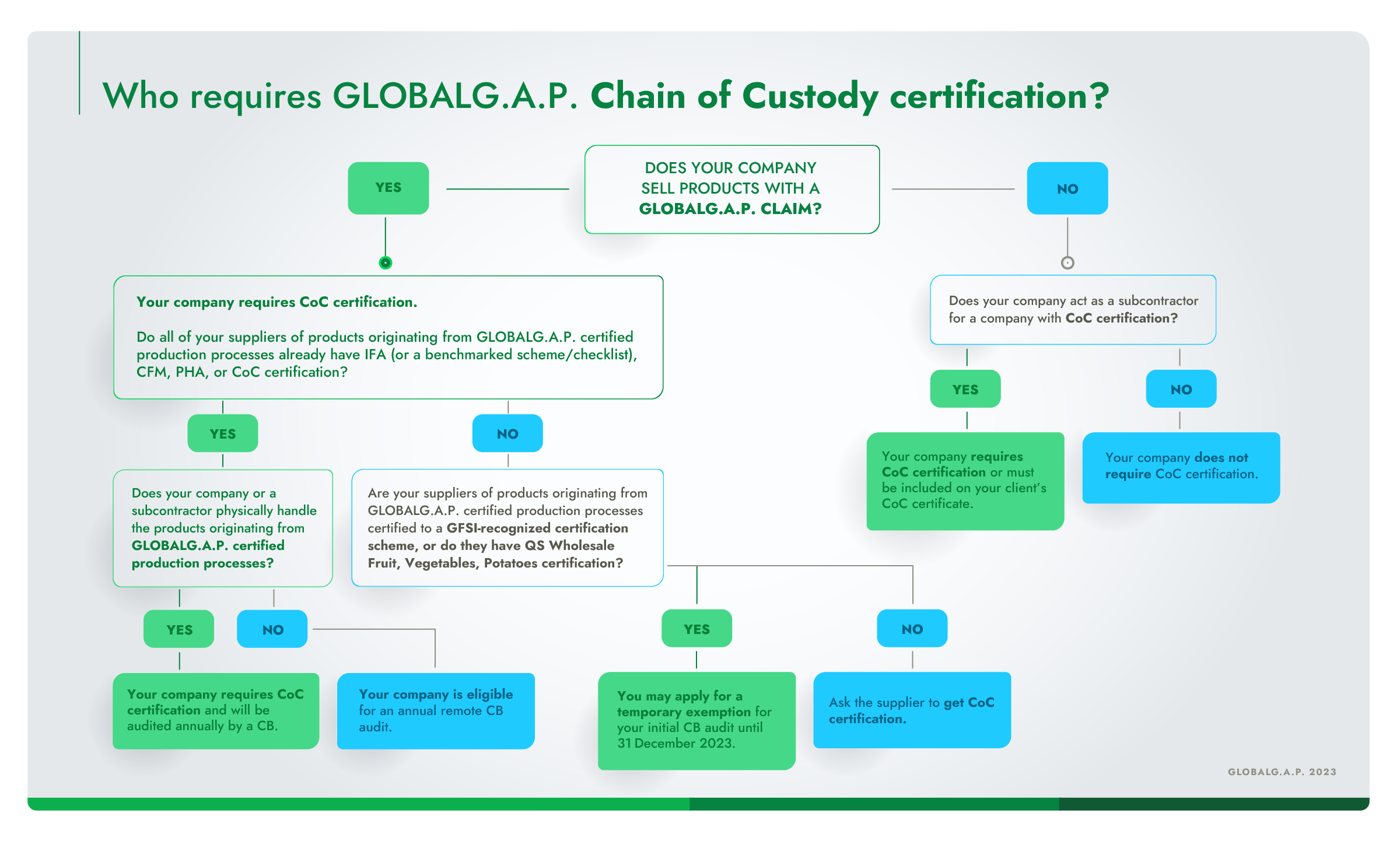
Specific requirements for supply chain companies
CoC does not apply to processes already included on the producer’s Integrated Farm Assurance (IFA) certificate. For example, it is not possible to have CoC certification for packing apples if product handling is included in the scope of the IFA certificate. It is, however, possible for the producer to have an IFA certificate for the apples they produce, as well as a CoC certificate for oranges that they only buy and sell.
Traders and brokers that wish to buy and sell products with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim must have CoC certification. Companies that trade products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes on behalf of a client with CoC certification (agencies, auctions, freight forwarders, etc.), but do not take ownership of the products, do not need CoC certification.
CoC certification is required for any company that transforms products and/or packs or repacks them after taking ownership. Contract processors, who process a product but do not take ownership of it, must have CoC certification unless they can be included in the scope of their client’s CoC certificate. If they are included in the client’s certificate scope, a CB audit is required. Processors, packers, and repackers are encouraged to have their own CoC certification even if they do not take ownership of the products.
CoC certification is required for retailers that buy and sell products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes if they wish to sell bulk products displayed with the GGN label visual elements. CoC certification is not required if all the products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes are sold by the retailer in consumer-ready and tamper-proof packaging.
Companies that transport products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes do not need CoC certification unless they take ownership of the products and are either involved in repacking/relabeling activities or involved in any kind of processing activity.
Companies that transport products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes on behalf of a client with CoC certification, but do not take ownership of the products, do not need CoC certification.
Companies such as cold stores which hold products in a storage area before processing, distributing, or selling must have CoC certification if they take ownership of the products. A subcontracted storage company’s activities may be audited as part of another client’s CoC certification. However, if they are involved in processing, repacking, or relabeling activities, a CB audit is required. Storage companies are encouraged to have their own CoC certification even if they do not take ownership of the products.
CoC certification is required for companies that display products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes which bear the consumer-facing GGN label visual elements. This includes companies that receive products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes in a prepackaged format but then subsequently open the packaging for on-site preparation.
Implementation and CB audit process
How does the CB audit process work?
CoC compliance is audited annually by accredited and independent third-party CBs.
Companies can choose from any GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB active in the relevant country.
A successful CB audit results in a certificate valid for one year.
The CB is responsible for uploading the audit report and maintaining the accuracy of company data in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform.
Companies will be audited annually by a CB as part of the renewal process.
Which documents are required?
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations: Rules that define how the certification process works, from the scope of the standard to the audit requirements.
Control points and compliance criteria (CPCCs): Control points are the fundamental requirements for each standard. They are written in question form and are accompanied by corresponding compliance criteria that detail the various ways in which a company can demonstrate compliance.
Checklist: The full list of CPCCs as used by CB auditors, enabling companies to conduct a self-assessment in preparation for the CB audit.
Which version of CoC is currently valid?
CoC v6.1 is the only valid version currently available for certification. It was published in November 2022 and replaced v6 on 1 July 2023.
The FAQ contains more information on documents, certification renewal, and more.

What are the CoC standard requirements?
CPCCs are graded in three levels: Major Must, Minor Must, and Recommendation.
To achieve certification, companies must comply with 100% of the Major Musts and at least one of the two Minor Musts.
Corrective actions must be proposed for all non-compliances and submitted to the CB within the specified period.
Non-compliances must then be verified as corrected and compliant by the CB before a certificate can be issued.
How much does CoC certification cost?
Each company is unique, and the total costs of certification depend on a combination of factors such as company size, number of sites, location, necessary preparation measures (such as establishing new procedures), and more. CoC contains three cost elements:
Implementation costs: Incurred by the company to prepare for the CB audit
CB service fees: Determined and invoiced by the CB to cover audit time and travel costs
GLOBALG.A.P. registration and certificate license fees: Annual fee invoiced by the CB for each registered and certified company
The GLOBALG.A.P. fee table contains full information on the fee structure for each standard and add-on.
Five steps to certification

You will need the CoC general regulations, the CoC CPCCs, and the checklist. All of the required documents are available online, for free, and in multiple languages. They are linked below and can also be found in the GLOBALG.A.P. document center.

Train staff and nominate your company’s CoC representative. Use the documents to guide the implementation of the standard requirements, and then conduct a self-assessment using the checklist. Our worldwide network of Registered Trainers can also provide assistance during audit preparations.

Search the list of GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs by region, country, scope, and status. Contact the CB of your choice and request an audit. Note that the GLOBALG.A.P. fee table does not cover CB service fees such as audit time or travel costs to your site.

The CB will conduct the audit and upload the results to the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform. Any non-compliances which are detected during the CB audit must be corrected within the specified period and verified by the CB before a certificate can be issued.

Once all requirements are met and verified by the CB, they will issue your CoC certificate. Your certification status is then publicly visible in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform for transparency in the market.
Key documents
The three most relevant documents are linked below. Click ‘view more’ to see further related documents. Remember to always check with your CB that you have all necessary documents prior to audit.
CoC
Checklists
V6.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
xlsx
Checklists
V6.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
xlsx
Checklists are documents containing standard/add-on principles and criteria which are used during the audit/assessment to check whether compliance is achieved. They may also be used to conduct self-assessments.
CoC
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations
V6.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations
V6.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations outline the framework of the certification system, including the role and relationship of the GLOBALG.A.P. Secretariat and certification bodies, and provide context for implementing checklist content.
CoC
Principles and criteria (P&Cs) (CPCCs)
V6.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Principles and criteria (P&Cs) (CPCCs)
V6.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Principles and criteria are a complete list of the requirements for a given standard or add-on. The foundational requirements each detail an outcome that must be achieved, and the corresponding ways in which compliance can be demonstrated.
GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs
The list of GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs can be filtered by region, country, scope, and status. Click a CB to find more information and contact details.
If you do not filter your search, or filter only according to region and/or country, your search results will also show CBs that offer certification against benchmarked schemes, but which may not have approval for any GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons.

Capacity building
Need assistance with the certification process? Our capacity-building program offers a range of options for training, consultation, and more!
A brief history of CoC
CoC development begins in 2004, and version 1 of the standard – applicable to aquaculture products only – is published in June 2005. The standard is revised and CoC v2 is launched in May 2008.
CoC v3 is released in January 2010, expanding the scope of products covered to include tea and coffee. CoC is made mandatory from the first postharvest processing step.
In 2013, CoC v4 is expanded to include fruit and vegetables, flowers and ornamentals, and more, in addition to aquaculture and livestock. In 2014, public consultation takes place for the revised CoC v5, which is launched in December.
By 2016, there are almost 500 CoC certificate holders. This number rises to 749 in 2017, handling more than five million metric tons of plants and two million metric tons of aquaculture products. By 2018, the number of CoC certificate holders passes 1,000, with certified companies in 38 countries. CoC v6 is published in September 2019, and by the end of the year, there are 1417 certificate holders across 45 countries worldwide.
The revision process for CoC v6 is initiated in 2021, and v6.1 is published in November 2022. It replaces v6 in July 2023. On 1 January 2023, new rules for supply chains are introduced, making CoC certification obligatory for all parties handling, packing, or labeling loose, unpacked products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes.
After this date, AGRAYA GmbH (formerly FoodPLUS GmbH) reserves the right not to conduct a full investigation on traceability problems or maximum residue limit exceedances connected to products with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim if the supply chain in question does not have full CoC certification at every step.
By the end of 2022, there are 3,342 CoC certificate holders in 55 countries, with this number rising to 4,274 certificate holders in 62 countries in 2023.
The number of CoC certificate holders continues to rise in 2024, reaching 5,137 across 65 countries.
FAQ
CoC v6.1 was published in November 2022 and replaced v6 on 1 July 2023.
From 1 January 2023, all parties who handle loose, unpacked products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes, as well as all parties who pack and label products with a GLOBALG.A.P. identification number (e.g., GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN), CoC Number) or make a written claim that a product originates from a GLOBALG.A.P. certified production process, are required to have valid CoC certification.
After this date, AGRAYA GmbH (formerly FoodPLUS GmbH) reserves the right not to conduct a full investigation on traceability problems or maximum residue limit exceedances connected to products with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim if the supply chain in question does not have full CoC certification at every step.
CB audits can be conducted remotely if a company meets both of the following criteria:
The company does not physically handle the products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes (for example, traders/brokers that do not take physical possession).
The company does not subcontract other companies to physically handle the products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes.
No, but the CoC standard specifies robust requirements for the implementation of segregation methods and traceability systems regarding products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes and those from noncertified production processes. These systems must be followed and will be audited by a certification body (CB).
Yes, although your chosen certification body (CB) is required to visit the site again when you begin handling and/or processing products from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes to check that the systems required by the standard are working appropriately.
Companies must inform their CB if they:
Identify a non-compliant product, for example, a product incorrectly labeled with a GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN) or CoC Number
Appoint a new staff member as the designated CoC representative
Undertake a new activity that is not already included in the certificate scope
Use a new subcontractor or packer that handles products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes
Add a new site to their company that is not included in the existing CoC certificate (as adding a new site to the certificate requires a full initial CB audit of the new site.)
Each company is unique, and the total cost of certification depends on a combination of factors such as size, location, existing policies and processes, etc. The invoice from your certification body (CB) will include CB service fees to cover expenditures (determined by the CB) and the GLOBALG.A.P. registration and certificate license fee.
Download the GLOBALG.A.P. fee table to learn more.
CoC documents are currently available in:
Dutch
English
French
German
Spanish
All documents are located in the GLOBALG.A.P. document center. More languages are added based on demand – please contact us with requests.
CoC compliance is audited annually. The certification body (CB) audit must take place within the validity period of the current certificate in order for your company to retain the certification status. Contact your CB to request an audit.
When developing our standards and add-ons, we aim to receive as much input and feedback as possible. With producers based in more than 135 countries around the world and stakeholders covering every part of the value chain, our standard-setting process ensures that our solutions are both fit for purpose now and built with the future in mind.
We offer public consultation periods for draft standard documents that are created by our technical experts. This helps uphold transparency in the development, revision, and decision-making processes. The web page on standard setting outlines the development process.
Technical questions can be addressed to standard_support@agraya.com. Your query will be forwarded to the relevant technical expert.
The GLOBALG.A.P. Academy offers public trainings on our portfolio of smart farm assurance solutions, while our worldwide network of Registered Trainers offers authorized trainings and other services. See the GLOBALG.A.P. Academy course catalog or find a Registered Trainer for more information.
The CB auditor requirements for CoC are detailed in the CoC general regulations.
Learn more about how to become a GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB or extend your auditing scope.
No, certification to a GLOBALG.A.P. standard/holding a GLOBALG.A.P. certificate is not the same as being a GLOBALG.A.P. Community Member.
GLOBALG.A.P. Community Membership is a paid partnership opportunity, offering a variety of benefits including the ability to support the development of GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons, contribute to the GLOBALG.A.P. governance structure, and access discounted services.
Learn more about how to become a GLOBALG.A.P. Community Member.
GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks may be used in a strictly B2B context and must be accompanied by a GLOBALG.A.P. identification number (e.g., the GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN), CoC Number) or a QR code to a company’s certification status in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform. The trademarks should never appear to consumers, for example on product packaging.
Download the GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks use: policy and guidelines and GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks use: FAQ documents for comprehensive information on rules and use cases.

Contact us
For technical/interpretation questions, please contact us at standard_support@agraya.com.
For questions about the audit process or the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform, please contact us at customer_support@globalgap.org.