
Core solution
Harmonized Produce Safety Standard
The Harmonized Produce Safety Standard (HPSS) is a robust food safety standard that includes the International Fresh Produce Association (IFPA) Produce GAP Harmonization Initiative’s Combined Harmonized Standard. It also contains additional content that is necessary to achieve certification recognized by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI).
Driving harmonization in food safety standards
What is the Harmonized Produce Safety Standard?
The Harmonized Produce Safety Standard (HPSS) is a global food safety standard covering both preharvest and postharvest production processes for fruit and vegetables and combinable crops. Aligned with the requirements of the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) Produce Safety Rule (PSR), the standard is applicable to producers who supply the US market. It offers a cost-efficient alternative to the flagship Integrated Farm Assurance (IFA) standard, as it only requires food safety elements. HPSS is the result of a collaboration with the International Fresh Produce Association (IFPA). Thanks to this collaboration, GLOBALG.A.P. can offer the only edition of the Produce GAP Harmonization Initiative’s Combined Harmonized Standard that is fully recognized by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) for fruit and vegetables. Applied in accordance with the GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations and integrity system, HPSS reduces audit fatigue in the supply chain by combining the GFSI v2020.1 benchmarking requirements for scope BI “Farming of Plants (Other Than Grains and Pulses)” into the same audit checklist.
HPSS at a glance
Offers GFSI-recognized
food safety-only certification (for fruit and vegetables) while reducing industry duplication
Covers the entire production process,
from preharvest activities through to postharvest handling
Includes verbatim
the Combined Harmonized Standard aligned with the PSR
Provides audit options
for a wide variety of farm sizes and types, including smallholders and producer groups
Results in
an accredited, third-party certificate which can be provided to value chain stakeholders such as importers
Designed specifically
for global fruit and vegetable and combinable crop producers who supply the US market
Offers GFSI-recognized
food safety-only certification (for fruit and vegetables) while reducing industry duplication
Provides audit options
for a wide variety of farm sizes and types, including smallholders and producer groups
Covers the entire production process,
from preharvest activities through to postharvest handling
Results in
an accredited, third-party certificate which can be provided to value chain stakeholders such as importers
Includes verbatim
the Combined Harmonized Standard aligned with the PSR
Designed specifically
for global fruit and vegetable and combinable crop producers who supply the US market
Which topics does HPSS address?
HPSS covers both preharvest and postharvest aspects of production. It consists primarily of the standards that collectively form the Produce GAP Harmonization Initiative’s Combined Harmonized Standard v2.0:
Field Operations and Harvesting Harmonized Standard v2.0
Post-Harvest Operations Harmonized Standard v2.0
For fruit and vegetable farms, additional HPSS control points specific to the BI scope of GFSI v2020.1 have been integrated into the standard. Traceability criteria unique to GLOBALG.A.P. certification are also included for both fruit and vegetables and combinable crops. HPSS is continuously developed in collaboration with the IFPA Harmonized Standard Technical Working Group and Calibration Committee to ensure that it remains robust, realistic, and cost-efficient for producers while meeting the evolving demands of buyers.
Core topics in HPSS v1.2 include:
Field production
Harvesting
Transportation (field to storage or packing house)
Postharvest operations
Transportation (packing house to customer)
Complaints
Food defense
Food fraud mitigation
Traceability and segregation
Mass balance
Discover more about how HPSS helps you address challenges in the agricultural sector.

Who should use HPSS?
HPSS is available globally for fruit and vegetable and combinable crop producers who supply the US market. It offers certification options for both individual producers (single site and multisite producers) and producer groups, including smallholders. Producers can get certification in any country where a GLOBALG.A.P. approved certification body (CB) conducts audits.
Producers can choose HPSS if they require a standard that only addresses food safety. GLOBALG.A.P.’s flagship Integrated Farm Assurance (IFA) standard – available for the product categories fruit and vegetables, combinable crops, and more – adopts a broader, holistic approach which also covers the key topics of environment and workers’ health, safety, and welfare.
Please note that fruit and vegetables is the only product category for which HPSS certification is recognized by GFSI. Producers of pulses, grains, and other crops that are machine-harvested (classified as “combinable crops” by GLOBALG.A.P. ) can get HPSS certification, but the resulting certificate is not recognized by GFSI.
How does HPSS work?
Compliance with the standard requirements is audited annually by an accredited and independent third-party CB.
Producers can choose from any GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB active in the relevant country.
A successful CB audit results in a certificate valid for one year.
The standard is composed of control points and compliance criteria (CPCCs). CPCCs are all graded at Major Must level, meaning that compliance with each point is mandatory.
Control points
Fundamentals that set the foundation of a GLOBALG.A.P. requirement
Written in question form
Compliance criteria
Methods that producers can use to demonstrate compliance
Evidence required for demonstrating that the outcome is achieved
Read more about the audit process and standard requirements.

How is certification status verified?
Every producer registered in the GLOBALG.A.P. certification system is assigned a 13-digit GLOBALG.A.P. identification number (in this case a Harmonized Produce Safety Standard GLOBALG.A.P. Number (HPSS-GGN)). This number allows verification of certification status in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform, upholding our rigorous transparency requirements throughout the supply chain.
Producers can control data access and privacy rights for audit reports, and the reports are not shared publicly or with third parties. This process is handled via your chosen CB.
What is the difference between IFA and HPSS?
| IFA | HPSS |
|---|---|
| Developed by stakeholders, for stakeholders in consultation with technical experts as part of the GLOBALG.A.P. standard setting process. | Developed by US stakeholders in the IFPA Harmonized Standard Technical Working Group, with additional content supplemented by GLOBALG.A.P. as necessary for GFSI recognition. |
| Adopts a holistic approach to certification, covering the key topics of food safety, environment, workers’ health, safety, and welfare, animal welfare, and traceability. | Only contains food safety criteria, supplemented with GLOBALG.A.P. traceability requirements. |
| Available for two scopes (plants and aquaculture) that contain multiple product categories (such as fruit and vegetables). | Only available for the product categories of fruit and vegetables and combinable crops. |
| Can be combined with the portfolio of GLOBALG.A.P. add-ons to core solutions, which are targeted at specific aspects of production and the supply chain. | Cannot be combined with the portfolio of GLOBALG.A.P. add-ons to core solutions, although CBs may offer commodity-specific metrics from the IFPA. |
| Audited by third-party, accredited, and GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs. | Audited by third-party, accredited, and GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs. |
| Requires the development of a food safety risk assessment. Under IFA, these protocols are called “mitigation procedures” and must take the form of a written policy. | Requires the development of a food safety risk assessment. Under HPSS, this is called a “food safety plan,” but not all documents take the form of a written policy. |
| Contains not only control points and compliance criteria, but also guidelines which provide producers with guidance on potential hazards to be identified and possible mitigation strategies. | Rather than guidance, the Combined Harmonized Standard refers to industry best practices. Auditing rules are not mandated, but set by each scheme operator, e.g., by GLOBALG.A.P.. |
Is HPSS compliant with the PSR?
Facilitated by the IFPA, the Harmonized Standard Technical Working Group aligned the Combined Harmonized Standard with the PSR in 2016.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released a statement in 2018 stating that the US Department of Agriculture’s Harmonized Good Agricultural Practices Audit Program (H-GAP) is aligned with the PSR. As this is formed of the same Combined Harmonized Standard that is included in full in HPSS, there is reasonable assurance that HPSS is also aligned.

Corporate news and events have moved!
All the latest updates can now be found on the Agraya website – connecting people, ideas, and solutions across the global farming network.
Looking for technical news?
Technical news updates for core solutions can be found in our technical news libraries.
Demonstrate your commitment to food safety
Why choose the Harmonized Produce Safety Standard?
The Harmonized Produce Safety Standard (HPSS) is a streamlined food safety standard that covers the entire production process and is recognized by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) for the production of fruit and vegetables. The standard is accepted by retailers in the US market and beyond who seek GFSI-compliant suppliers, with the HPSS certificate demonstrating producer commitment to responsible food safety practices in farming, as well as efforts towards the implementation of the requirements of the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA).
Which industry challenges does HPSS address?
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 48 million people in the United States – one in six – suffer from foodborne illnesses each year.
FSMA was introduced by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to shift the attention from responding to food safety issues to preventing them, viewing the topic as not only a public health problem but also a threat to the long-term sustainability of the food supply chain.
The FDA now requires all importers of fresh produce to the US market to apply the FSMA rules through the Foreign Supplier Verification Program (FSVP) – ensuring that these products meet consistent science-based standards for food safety, preventive controls, and more.
In 2009, the International Fresh Produce Association (IFPA) founded the Produce GAP Harmonization Initiative with the goal to “reduce audit fatigue and allow operations to focus their food safety resources on achieving food safety, rather than passing audits.”
Combined with growing requests from GLOBALG.A.P. stakeholders for a dedicated food safety standard that is recognized by GFSI, HPSS was created to offer the Produce GAP Harmonization Initiative’s Combined Harmonized Standard via the GLOBALG.A.P. certification system – achieving the goal of “one audit by a credible third party, acceptable to all buyers.”
Follow our five steps to certification to get started today.
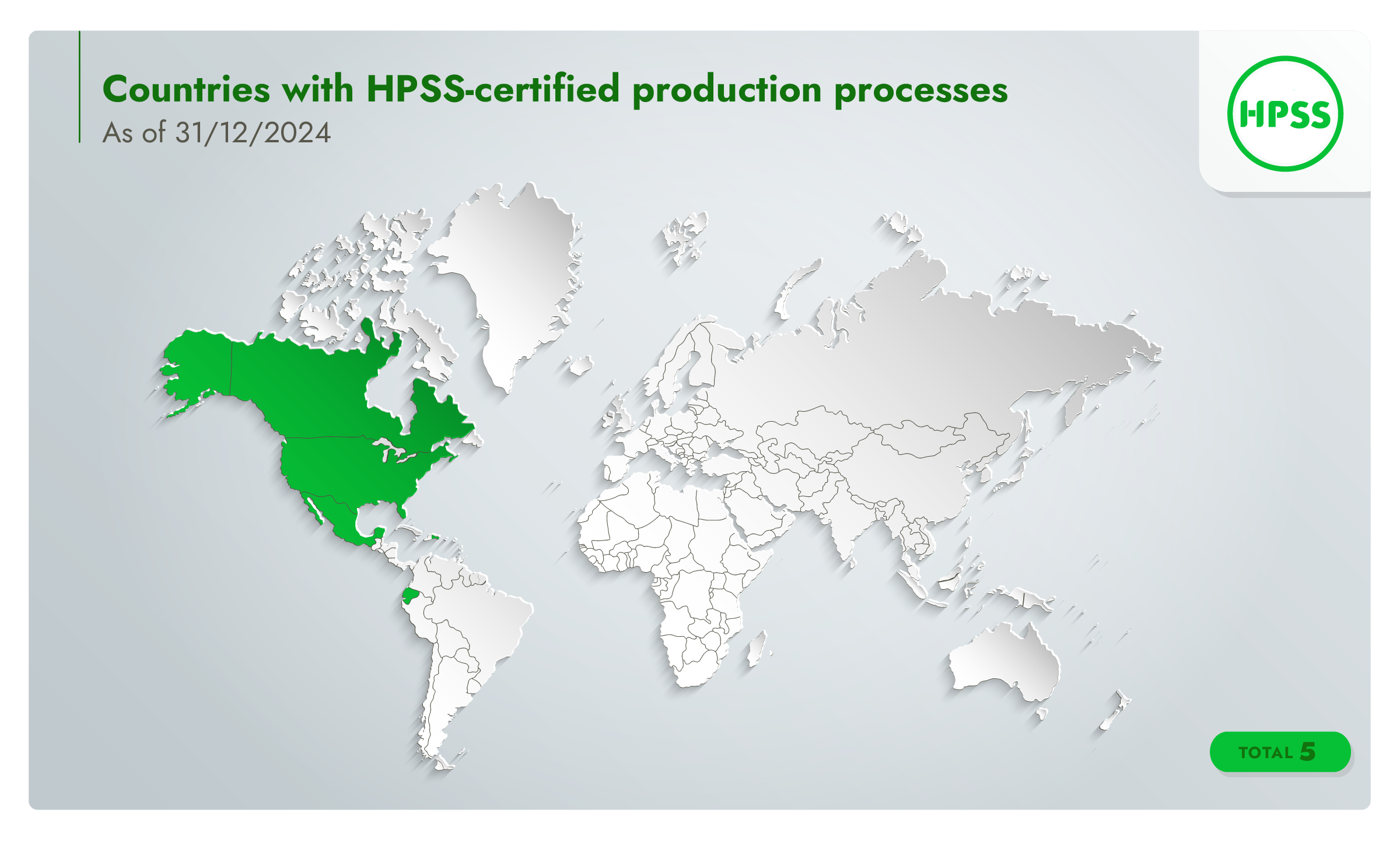
HPSS in numbers (as of 31/12/2024)
323
producers under certification
5
countries with certified production processes
37,056
hectares of certified production
323
producers under certification
5
countries with certified production processes
37,056
hectares of certified production

What are the benefits for producers?
Improve food safety-related farm management and mitigate reputational risks.
Achieve compliance with a globally recognized standard, benchmarked by GFSI for fruit and vegetables, that fulfills international supply chain requirements.
Apply our smart farm assurance solutions on a wide range of farm types and sizes and access certification options for both individual producers and producer groups.
Choose from an extensive worldwide network of accredited, GLOBALG.A.P. approved certification bodies (CBs).
Provide the certificate to importers, retailers, and other value chain stakeholders as third-party verified evidence of your efforts towards FSMA implementation.

What are the benefits for supply chain stakeholders?
Support industry-driven smart farm assurance solutions – developed by the sector, for the sector – that reduces the audit burden and enables buyers to easily identify suppliers that fulfill their requirements.
Mitigate food safety-related reputational risks, with added GLOBALG.A.P. traceability requirements that seek to protect product integrity.
Source from a growing pool of suppliers with certified production processes globally, with easy certification verification in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform.
Receive third-party verified evidence of supplier efforts towards FSMA implementation.

Maintaining trust in GLOBALG.A.P. certification
The GLOBALG.A.P. Integrity Program was founded in 2008 as the first of its kind in food certification. Designed to ensure the consistent delivery and implementation of GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons worldwide, the program monitors and assesses all aspects of the third-party certification process.
Which solutions can be combined with HPSS?
As HPSS is based on the Produce GAP Harmonization Initiative’s Combined Harmonized Standard, it cannot be combined with GLOBALG.A.P. add-ons to core solutions. However, the GLOBALG.A.P. portfolio of smart farm assurance solutions offers two other solutions that address the FSMA requirements for producers based in or supplying the US market.
Learn more about GLOBALG.A.P. smart farm assurance solutions.
You may also be interested in...
Integrated Farm Assurance for fruit and vegetables
IFA is a global standard that aims to promote safer and more responsible farming practices in fruit and vegetable production.
Produce Handling Assurance
PHA is a GFSI-recognized, FSMA-aligned food safety and traceability standard for postharvest activities such as the packing, handling, and storage of crops.
Food Safety Modernization Act Produce Safety Rule add-on
The FSMA PSR add-on addresses FDA requirements for the import of fruit and vegetable products to the US market.
Your guide to implementation
How to prepare for a Harmonized Produce Safety Standard audit
Learn more about the key documents and fee structure of the Harmonized Produce Safety Standard (HPSS). Follow our five steps to certification for an overview of the certification process, and find a GLOBALG.A.P. approved certification body (CB) in your area to get started.
Implementation and CB audit process
How does the CB audit process work?
HPSS compliance is audited annually by accredited and independent third-party CBs.
Producers can choose from any GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB active in the relevant country.
A successful CB audit results in a certificate valid for one year.
The CB is responsible for uploading the audit report and maintaining the accuracy of producer data in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform.
Producers will be audited annually by a CB as part of the renewal process.
Which documents are required?
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations and its addendum for HPSS: Rules that define how the certification process works, from the scope of the respective standard to the audit requirements.
Control points and compliance criteria (CPCCs): Control points are the fundamental requirements for each standard. They are written in question form and are accompanied by corresponding compliance criteria that detail how a producer must demonstrate compliance.
Checklist: The full list of CPCCs as used by CB auditors, enabling producers to conduct a self-assessment in preparation for the CB audit.
Which version of HPSS is currently valid?
HPSS is currently valid in version 1.2.
HPSS v1.2 was published in August 2020 and replaced all previous versions in November 2020. In May 2021, it achieved renewed recognition from the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) for fruit and vegetables, having been successfully benchmarked against GFSI’s Benchmarking Requirements Version 2020.1. The standard first completed the GFSI benchmarking process in 2016.
The revision of the standard for v2 is currently ongoing and is due for publication in 2026.
The FAQ contains further information on documents, certification renewal, and more.

What are the HPSS requirements?
CPCCs are all graded as Major Musts.
To achieve certification, producers must comply with 100% of the Major Musts.
Corrective actions must be proposed for all non-compliances and submitted to the CB within the specified period.
Non-compliances must then be verified as corrected and compliant by the CB before a certificate can be issued.
How much does HPSS certification cost?
Each farm is unique, and the total costs of certification depend on a combination of factors such as farm size, number of sites, location, necessary preparation measures (such as establishing new procedures), and more. HPSS contains three cost elements:
Implementation costs: Incurred by the producer to prepare for the CB audit
CB service fees: Determined and invoiced by the CB to cover audit time and travel costs
GLOBALG.A.P. registration and certificate license fee: Calculated based on farm size and invoiced by the CB
The GLOBALG.A.P. fee table contains full information on the fee structure for each standard and add-on.
Five steps to certification

You will need the GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations and its addendum for HPSS, the HPSS CPCCs, and the checklist. All the required documents are available online, for free, and in multiple languages. They are linked below and can also be found in the GLOBALG.A.P. document center.

Use the documents to guide the implementation of the standard requirements, and then
conduct a self-assessment using the checklist. Our worldwide network of Registered Trainers
can also provide assistance during audit preparations.

Search the list of GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs by region, country, scope, and status. Contact the CB of your choice and request an audit. Note that the GLOBALG.A.P. fee table does not cover CB service fees such as audit time or travel costs to your site.

The CB will conduct the audit and upload the results to the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform. Any non-compliances which are detected during the CB audit must be corrected within the specified period and verified by the CB before a certificate can be issued.

Once all requirements are met and verified by the CB, they will issue your HPSS certificate. Your certification status is then publicly visible in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform for transparency in the market.
Key documents
The three most relevant documents are linked below. Click ‘view more’ to see further related documents. Remember to always check with your CB that you have all necessary documents prior to audit.
HPSS
Checklists
V1.2
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
xlsx
Checklists
V1.2
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
xlsx
Checklists are documents containing standard/add-on principles and criteria which are used during the audit/assessment to check whether compliance is achieved. They may also be used to conduct self-assessments.
HPSS
Principles and criteria (P&Cs) (CPCCs)
V1.2
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Principles and criteria (P&Cs) (CPCCs)
V1.2
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Principles and criteria are a complete list of the requirements for a given standard or add-on. The foundational requirements each detail an outcome that must be achieved, and the corresponding ways in which compliance can be demonstrated.
HPSS addendum to GR
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations
V1.2
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations
V1.2
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations outline the framework of the certification system, including the role and relationship of the GLOBALG.A.P. Secretariat and certification bodies, and provide context for implementing checklist content.
GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs
The list of GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs can be filtered by region, country, scope, and status. Click a CB to find more information and contact details.
If you do not filter your search, or filter only according to region and/or country, your search results will also show CBs that offer certification against benchmarked schemes, but which may not have approval for any GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons.

Capacity building
Need assistance with the certification process? Our capacity-building program offers a range of options for training, consultation, and more!
A brief history of HPSS
In June 2009, the US-based International Fresh Produce Association (IFPA, formerly the United Fresh Food Safety Council) puts forward a plan to drive the harmonization of Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) standards in the fresh produce industry. The collaboration involves a range of value chain stakeholders – such as producers, buyers, government agencies, CBs, and more – and results in the formation of the Produce GAP Harmonization Initiative.
The initiative develops the food safety-focused Combined Harmonized Standard with the goal of “one audit by a credible third party, acceptable to all buyers,” covering preharvest and postharvest operations and applicable to all fresh produce commodities and all sizes of farms. Version 1 of the Combined Harmonized Standard is published in 2011.
To answer the demand from stakeholders for a food safety-only standard with GFSI recognition, GLOBALG.A.P. licenses the Combined Harmonized Standard, adds the necessary GFSI benchmarking requirements and additional traceability criteria, and uses an amended version of the GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations to enable CBs to seamlessly offer both standards.
HPSS v1 is published in June 2014.
HPSS completes the GFSI benchmarking process for the first time in 2016, achieving recognition for the fruit and vegetables scope. It is the first GFSI-recognized standard from the industry-wide harmonization initiative for the North American market.
By the end of 2018, there are 67 producers under HPSS certification across the United States, Mexico, and Ecuador. The standard revision process begins for v1.1.
HPSS v1.1, with updated CPCCs and addendum to the GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations, is published in January 2019, replacing v1 in April 2019. It is subsequently updated to v1.1-2 in September 2019. By the end of the year, there are 125 producers under HPSS certification in four countries.
HPSS v1.2 is published in August 2020, replacing v1.1-2 in November 2020. By the end of 2020, there are 179 producers under HPSS certification. GLOBALG.A.P. reapplies for GFSI recognition, and consultation begins in February 2021.
In May 2021, HPSS achieves renewed GFSI recognition, having been successfully benchmarked against GFSI’s Benchmarking Requirements Version 2020.1.
By the end of 2022, there are 197 producers under HPSS certification in five countries. The revision process for v2 begins in May 2023, with an estimated publication date for the new version of the standard in 2026.
In 2024, there are more than 37,000 hectares of production under certification.
FAQ
HPSS is currently valid in version 1.2. It was published in August 2020 and replaced all previous versions in November 2020. In May 2021, it achieved renewed recognition from the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) for fruit and vegetables, having been successfully benchmarked against GFSI’s Benchmarking Requirements Version 2020.1.
HPSS is the abbreviation for the GLOBALG.A.P. Harmonized Produce Safety Standard.
Harmonized GAP is a common name used to refer to the Produce GAP Initiative’s Combined Harmonized Standard, with H-GAP used as the acronym.
Stakeholders often mistakenly refer to the United States Department of Agriculture Harmonized GAP (USDA H-GAP) as the only H-GAP. In reality, there are over 14 certification schemes that offer the Combined Harmonized Standard. While the content of the standard remains the same across all H-GAP schemes, H-GAP does not specify audit rules. These are developed independently by each organization.
HPSS is audited based on the existing, industry-leading GLOBALG.A.P. certification system, enforcing the same GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations and integrity requirements that apply to all of our standards and add-ons. HPSS is the only version of H-GAP that is ISO 17065-accredited for approved certification bodies (CBs).
Yes, HPSS is the only version of the Combined Harmonized Standard (H-GAP) that is GFSI-recognized for fruit and vegetables. It first achieved benchmarked status in 2016 and went through a successful reapplication process in 2021.
Producers of combinable crops may achieve certification to HPSS, but the resulting certificate is not recognized by GFSI.
According to GFSI, “Private Certification Programmes may achieve GFSI recognition through benchmarking of their governance rules and the content of their standard. Government-owned standards may be acknowledged through benchmarking of their standard.”
Government-owned standards (such as the United States Department of Agriculture Harmonized GAP (USDA H-GAP)) that apply for GFSI benchmarking can achieve “technical equivalence”. In practice, the food safety requirements in the audit criteria meet the GFSI benchmarking criteria for the relevant scope; however, the applicant entity is not required to benchmark governance rules.
Standard governance includes criteria such as corrective action timelines, auditor qualifications, report review and certification procedures, or rules for granting certification to producer groups or multisite producers. Only those certification programmes that have “recognition” have been benchmarked for both the standard and the accompanying audit program rules.
The International Fresh Produce Association’s Harmonized Standard Technical Working Group aligned the Combined Harmonized Standard to the PSR in 2016.
In 2018, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) then released a statement stating that the US Department of Agriculture’s Harmonized Good Agricultural Practices Audit Program (H-GAP) is aligned with the PSR. As this is formed of the same Combined Harmonized Standard that is included in full in HPSS, there is reasonable assurance that HPSS is also aligned. However, it is currently not formally recognized by the FDA.
IFA is GLOBALG.A.P.’s flagship standard, developed by GLOBALG.A.P. stakeholders and available and accepted globally.
IFA adopts a holistic approach to responsible farming practices, also incorporating criteria aimed at addressing environmental and social topics alongside food safety.
IFA is available for fruit and vegetables and combinable crops, as well as other plant product categories, and aquaculture.
IFA enables producers to flexibly extend the certification scope through a portfolio of add-ons to core solutions targeting specific aspects of production and the supply chain.
HPSS is based on the Produce GAP Initiative’s Combined Harmonized Standard, owned by the International Fresh Produce Association (IFPA).
HPSS only focuses on food safety topics: It does not include environmental or social responsibility criteria.
HPSS includes, verbatim, the language of the Combined Harmonized Standard as developed by the IFPA Harmonized Standard Technical Working Group, of which GLOBALG.A.P. is a working member.
HPSS is only available for fruit and vegetables and combinable crops, and the GLOBALG.A.P. portfolio of add-ons cannot be applied to HPSS.
Both IFA and HPSS audits are offered by ISO 17065–accredited and GLOBALG.A.P. approved certification bodies (CBs).
Each farm is unique, and the total cost of certification depends on a combination of factors (such as size, location, existing policies and processes, etc.). The invoice from your certification body (CB) will include CB service fees to cover expenditures (determined by the CB) and the GLOBALG.A.P. registration and certificate license fee.
Download the GLOBALG.A.P. fee table to learn more.
HPSS documents are currently available in:
English
Spanish
All documents are located in the GLOBALG.A.P. document center. More languages are added based on demand – please contact us with requests.
HPSS compliance is audited annually. The certification body (CB) audit must take place within the validity period of the current certificate in order for you to retain your certification status. Contact your CB to request an audit.
The Produce GAP Harmonization Initiative’s Combined Harmonized Standard goes through a revision process in collaboration with the International Fresh Produce Association (IFPA) Harmonized Standard Technical Working Group and Calibration Committee every three years. GLOBALG.A.P. regularly participates in Calibration Committee meetings.
Interim changes may also be proposed by the Harmonized Standard Technical Working Group and Calibration Committee according to industry feedback and the publication of regulations (e.g., the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) Produce Safety Rule (PSR) agricultural water requirements).
The latest revision of the Combined Harmonized Standard began in August 2022 and resulted in v3.0, published in May 2023. The GLOBALG.A.P. HPSS will have one year to transition to the new v3.0 (May 2024). The next revision for the Combined Harmonized Standard will begin in 2025, with an estimated publication date for v4.0 in early 2026.
Technical questions can be addressed to standard_support@agraya.com. Your query will be forwarded to the relevant technical expert.
The GLOBALG.A.P. Academy offers public training courses on our portfolio of smart farm assurance solutions, while our worldwide network of Registered Trainers offers authorized training courses and other services. See the GLOBALG.A.P. Academy course catalog or find a Registered Trainer for more information.
The CB auditor requirements for HPSS are detailed in “Harmonized Produce Safety Standard general regulations".
Learn more about how to become a GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB or extend your auditing scope.
No, certification to a GLOBALG.A.P. standard/holding a GLOBALG.A.P. certificate is not the same as being a GLOBALG.A.P. Community Member.
GLOBALG.A.P. Community Membership is a paid partnership opportunity, offering a variety of benefits including the ability to support the development of GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons, contribute to the GLOBALG.A.P. governance structure, and access discounted services.
Learn more about how to become a GLOBALG.A.P. Community Member.
GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks may be used in a strictly B2B context and must be accompanied by a GLOBALG.A.P. identification number (e.g., the producer’s GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN)) or a QR code to a producer’s certification status in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform. The trademarks should never appear to consumers, for example on product packaging.
Download the GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks use: policy and guidelines and GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks use: FAQ documents for comprehensive information on rules and use cases.
Questions about FSMA?
See our dedicated FAQ for information on FSMA rules for the fresh produce industry, including producers, postharvest facilities, importers, and certification bodies.

Contact us
For technical/interpretation questions, please contact us at standard_support@agraya.com.
For questions about the audit process or the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform, please contact us at customer_support@globalgap.org.